# Class01
## Introduction to WRDS
### History
- Constructed by Wharton in **1993**
- Written by SAS
- To facilitate data collection and data analysis for finance research
### Development
- WRDS cloud and Postgres connection are developed over past few years
- More than **350TB** data
- Over **500** subscribers
### WRDS access
- Register WRDS account
1\. Go to WRDS
2\. Click **REGISTER** on top right
3\. Fill registration form and then submit
- Access methods
- Web interface
- WRDS cloud (SSH)
- Computer language/software (Python, R, SAS, Stata)
## Introduction to Python
### Install Anaconda
1\. Go to Anaconda
2\. Scroll down to find the installation files

Choose the operating system (Linux/MacOS/Windows) and make sure to download the **64-bit Graphical Installer**
3\. Double click the installation file and follow the wizard to complete the installation
```{seealso}
Anaconda installation tutorial Youtube video from Ties
```
### Python editors
#### Jupyter Notebook
1\. Open your terminal (MacOS) or start Anaconda prompt (Windows), then type in `jupyter lab`. This will open notebook in your default web browser.
2\. Click **Python3**
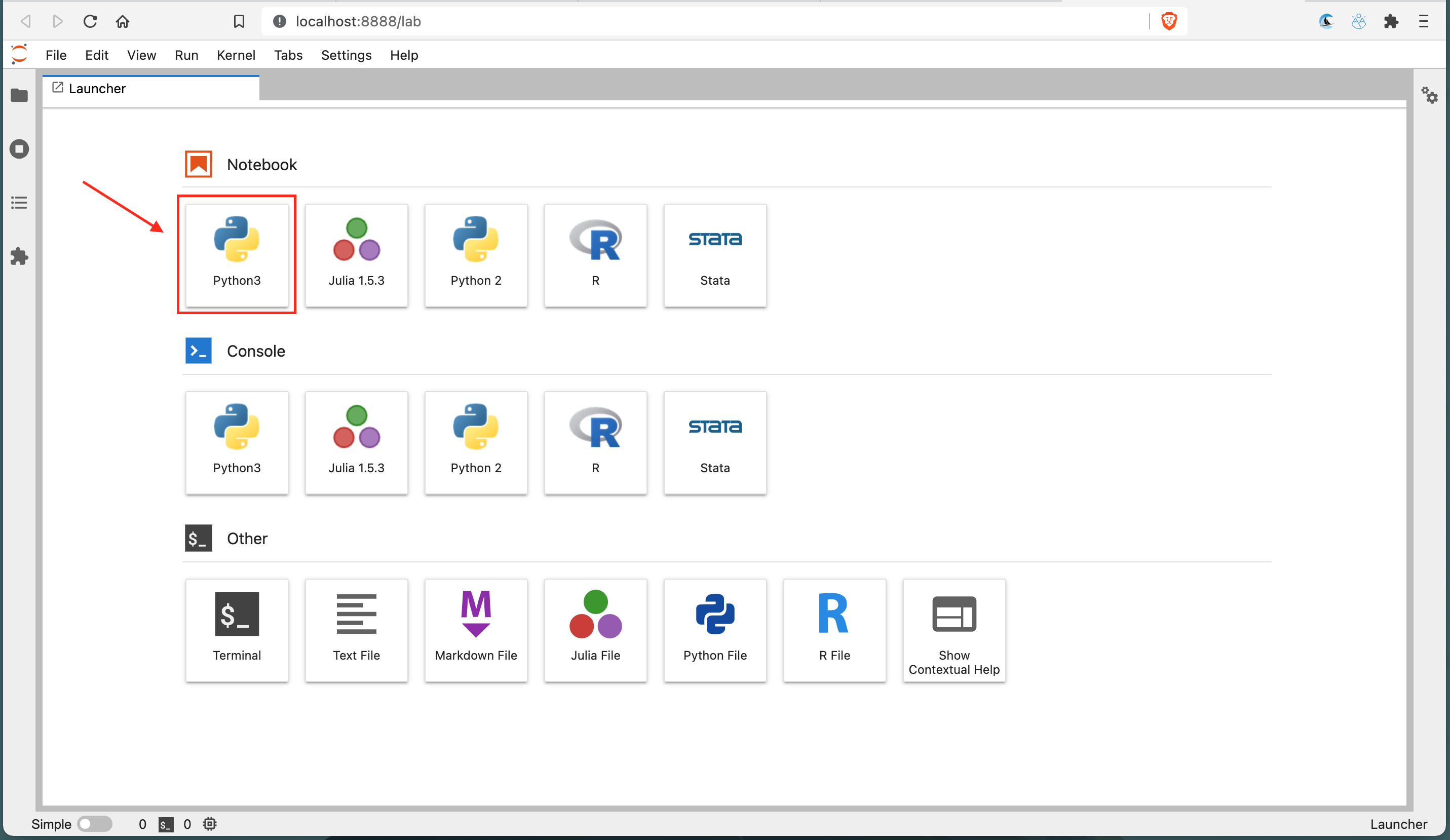
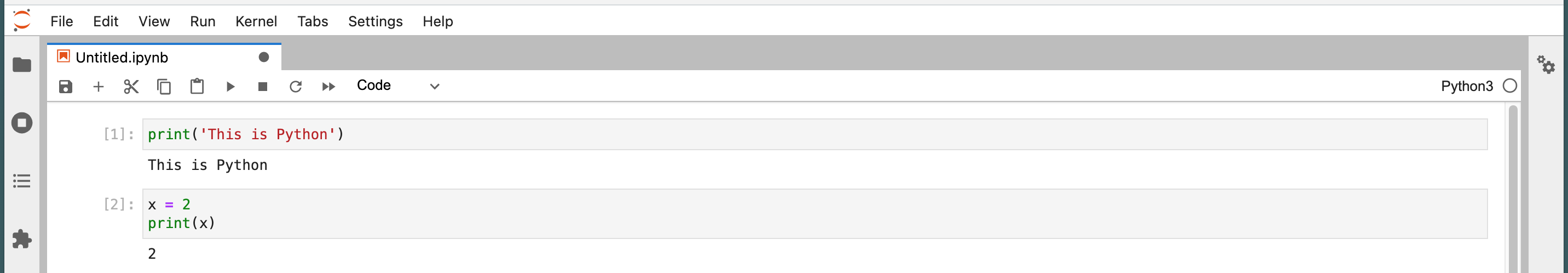
3\. Type in `print('This is Python')` in the first cell and press shift + enter (this is the keyboard shortcut to run the code in that cell). The string will be printed out below. In the second cell, let's write mutiple lines code and run it. In the example below, 2 will be printed.
#### VSCode
There are many other ways to execute Python code. VSCode is a very popular one.
1\. Visit VSCode to download installation file and install it.
2\. Start VSCode and click the icon on the left bar as indicated below
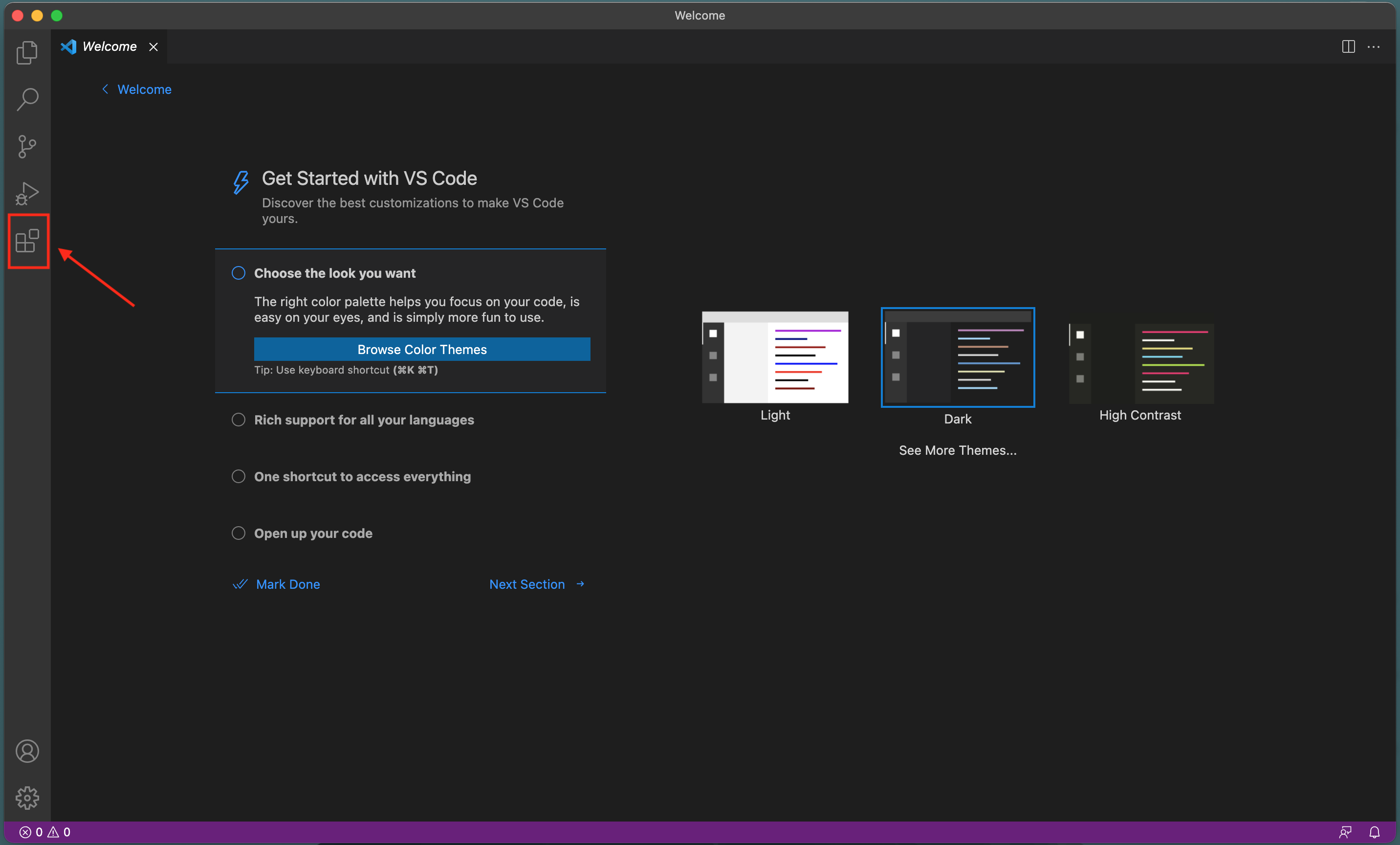
3\. You will find Python extension and click **install**.
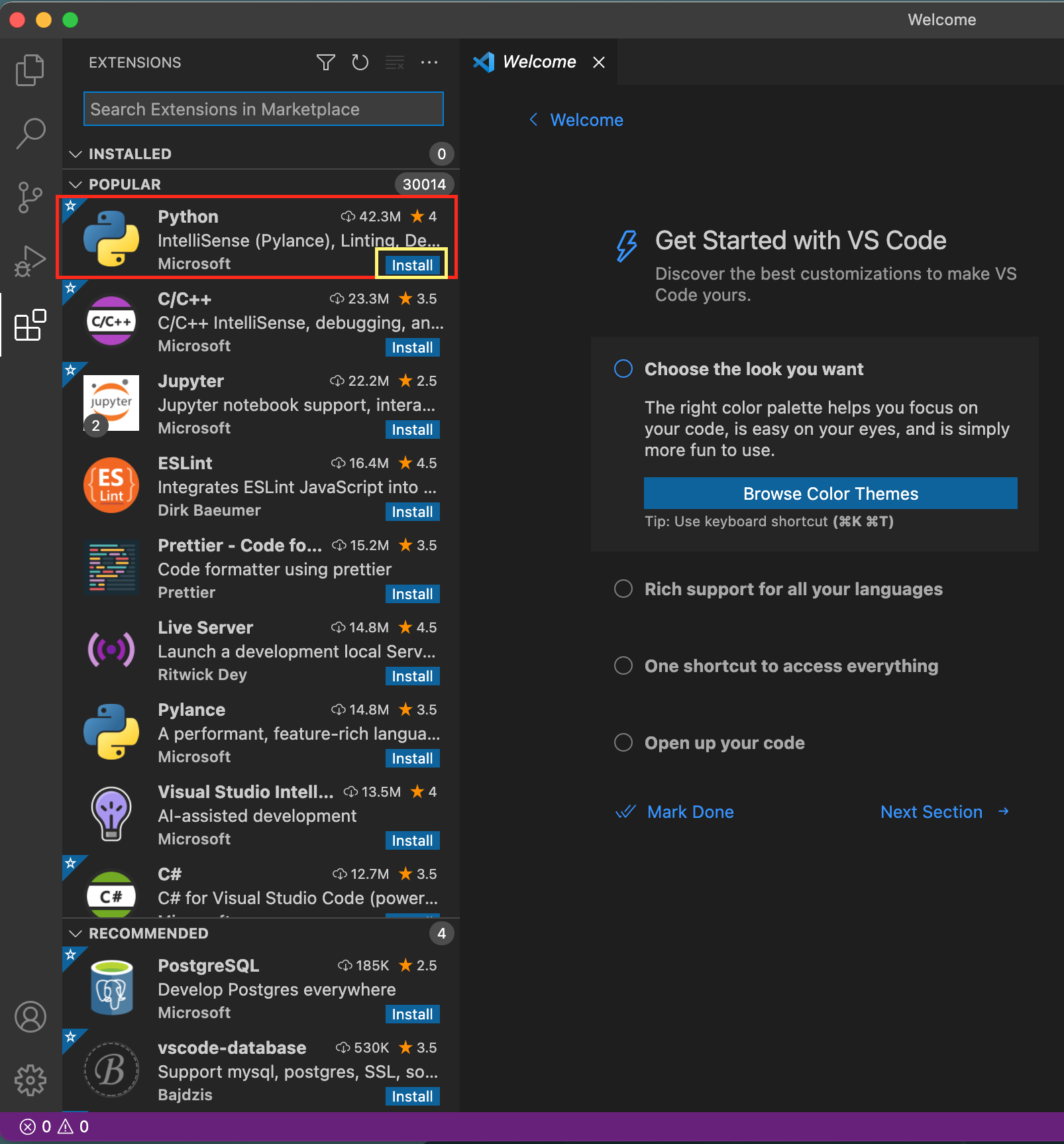
4\. Please type in `python` in the search bar if you cannot see the extension.
5\. cmd+n (MacOS) or alt+n (Windows) to create a new file, type in `print('This is Python')` and save the file with the extension of **.py**.
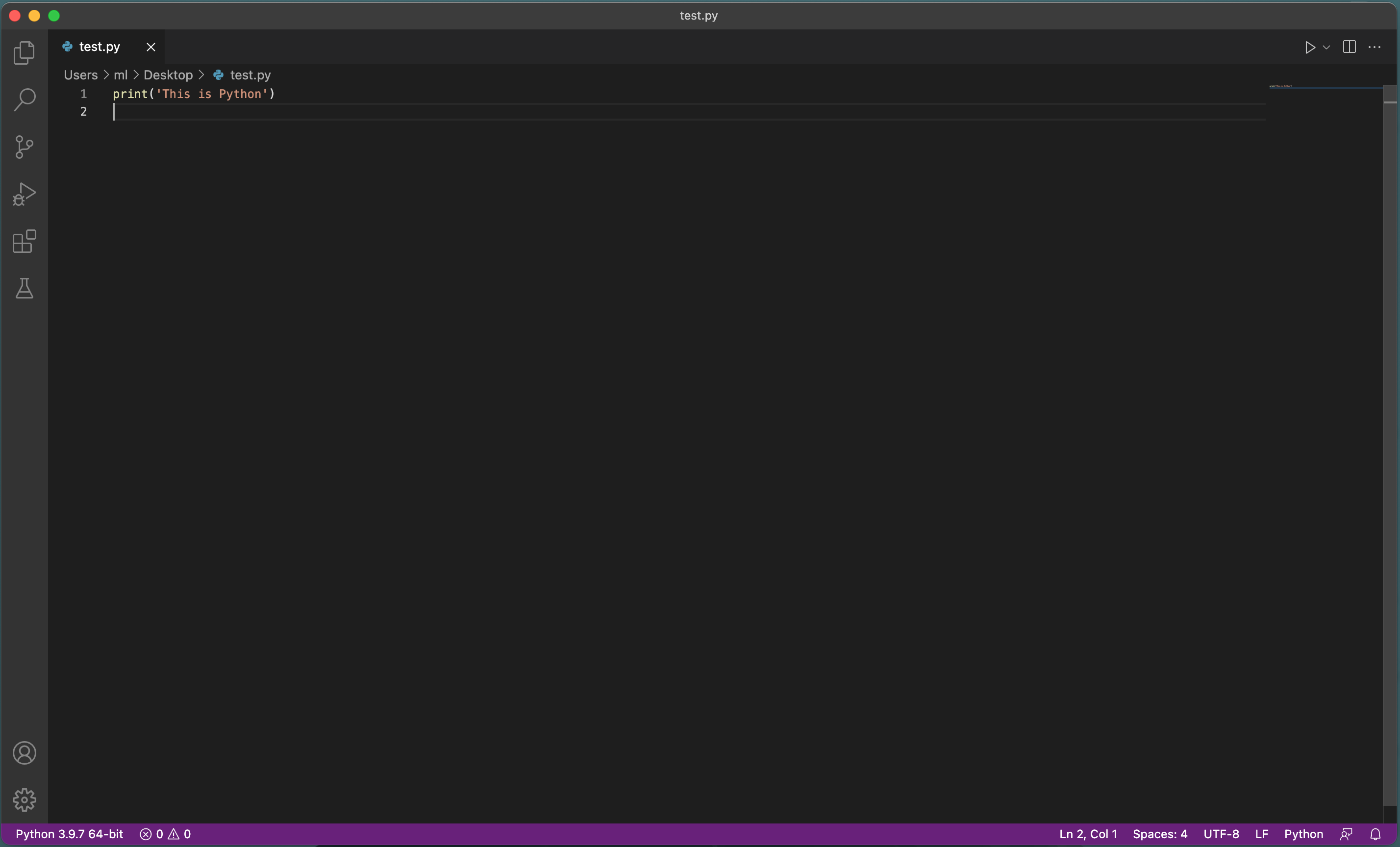
6\. Check if you have the Anaconda version of Python at left bottom corner. Just click it if you are not sure the Python version. Choose the Python version with anaconda path.
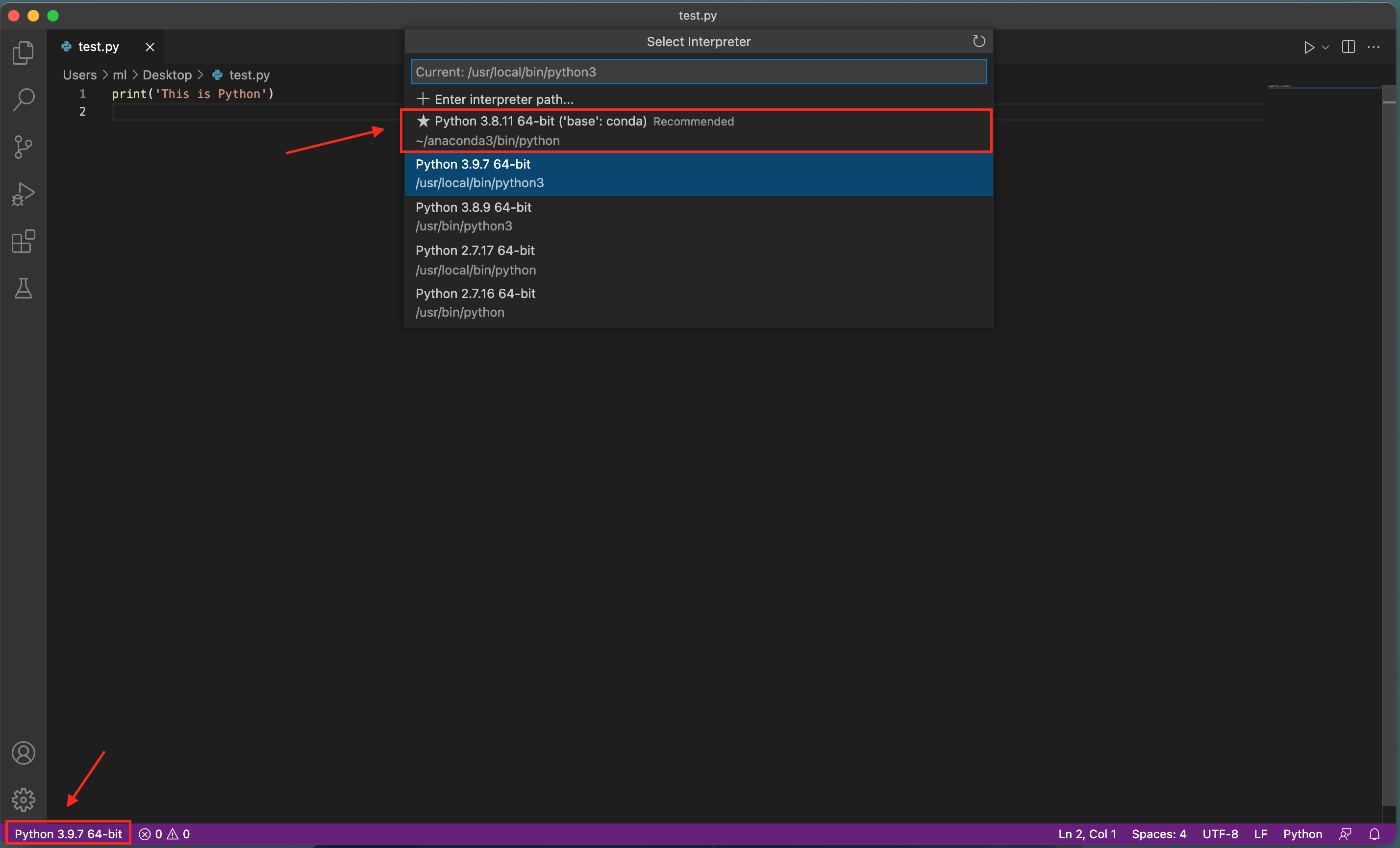
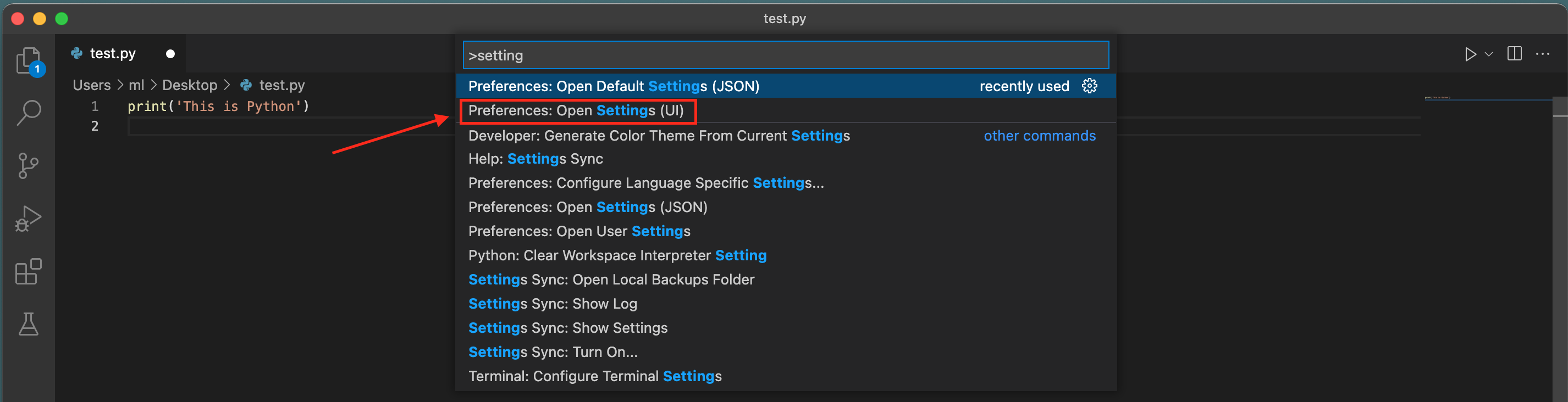
7\. cmd+shift+p (MacOS) or ctrl+shift+p to open command palette. Type in `setting` and click **Preferences: Open Setting (UI)**.
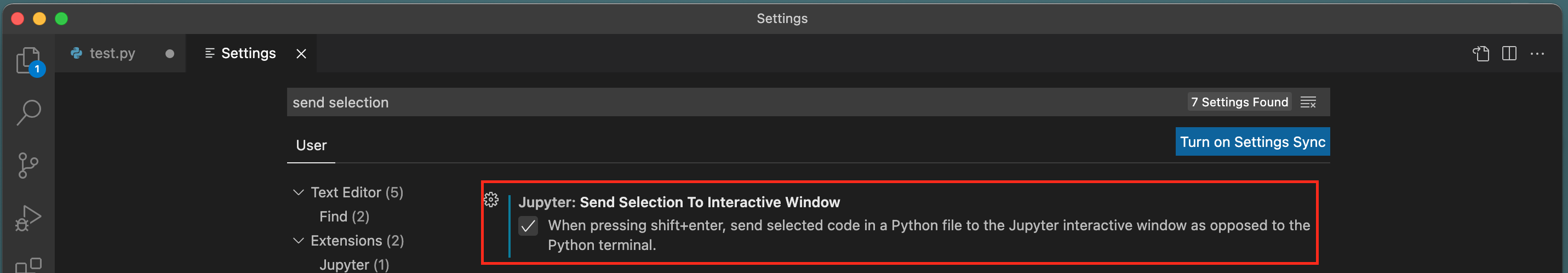
8\. Type in `send selection` in the search on top and make sure **Jupyter: Send Selection to Interactive Window** is ticked.
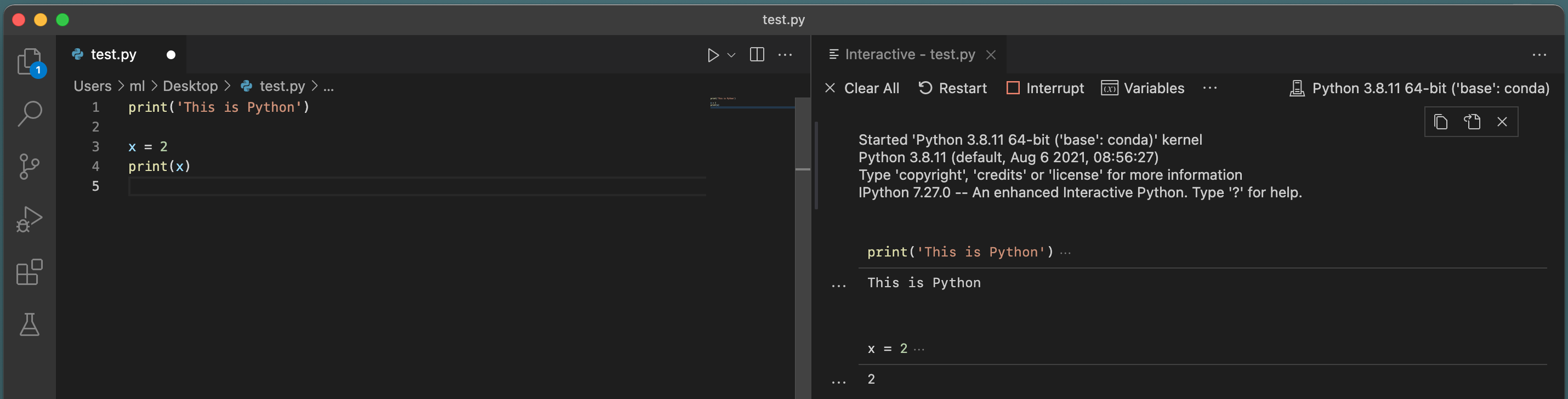
9\. Move your cursor anythere in the fisrt line and press shift+enter, then an interactive window will be pop up on the right and the result will be printed there. For multiple line code, just select all the codes first and then press shift+enter to run the selection. You will see the results on the right.
#### Other editors
- **Spyder**. This is included in Anaconda distribution (video tutorial)
- **Vim** (an article how to build a Python IDE in **Vim**)
- **Emacs** (an article how to configure a Python environment in **Emacs**; **Doom Emacs** is an out-of-box configuration)
```{note}
There is a learning curve to use **Emacs** and **Vim** if you have no previous experience. Therefore, have a try only if you are interested in **Emacs** and **Vim**. Both of them have unique features to make your empirical research more productive. You can also see my **Emacs** configuration (.emacs.d).
I use **Emacs** to do all my empirical research.
```
### Retrieve WRDS data
WRDS provides Python package **wrds** to make our life much easier to download data from WRDS (the package is kind of wrapper of postgres connction to WRDS).
**Click the binder icon below to lanuch the notebook of class01**
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/mk0417/financial-database/master)
- Import required packages
```{code-block} python
import wrds
import pandas as pd
```
- Connect to WRDS
```{code-block} python
conn = wrds.Connection()
```
After you run it, type in your WRDS username and press enter; type in your WRDS password and press enter
- List databases
```{code-block} python
lib = conn.list_libraries()
# view first 3 databases
lib[:3]
```
- List tables
```{code-block} python
# get tables from CRSP database
table = conn.list_tables('crsp')
# view first 3 tables
table[:3]
```
- Describe tables
```{code-block} python
# list variables in monthly stock file (msf) from CRSP
conn.describe_table('crsp', 'msf')
```
- Extract data
```{code-block} python
msf = conn.raw_sql("""
select permno, date, ret
from crsp.msf
where date>='01/01/2020' and date<='05/31/2020'
""")
# list first 5 observations
msf.head()
```
SQL syntax
- select
- claim which variables you want to download and seprate them by comma (,)
- from
- declare which table the variables are from
- where
- conditional statement (like a filter)
```{seealso}
Learn more SQL from PostgreSQL tutorial
```